
They are employed as sweeteners and in the manufacture of perfumes, as well as being important intermediates in the synthesis of other compounds.
#Alcohol functional group series#
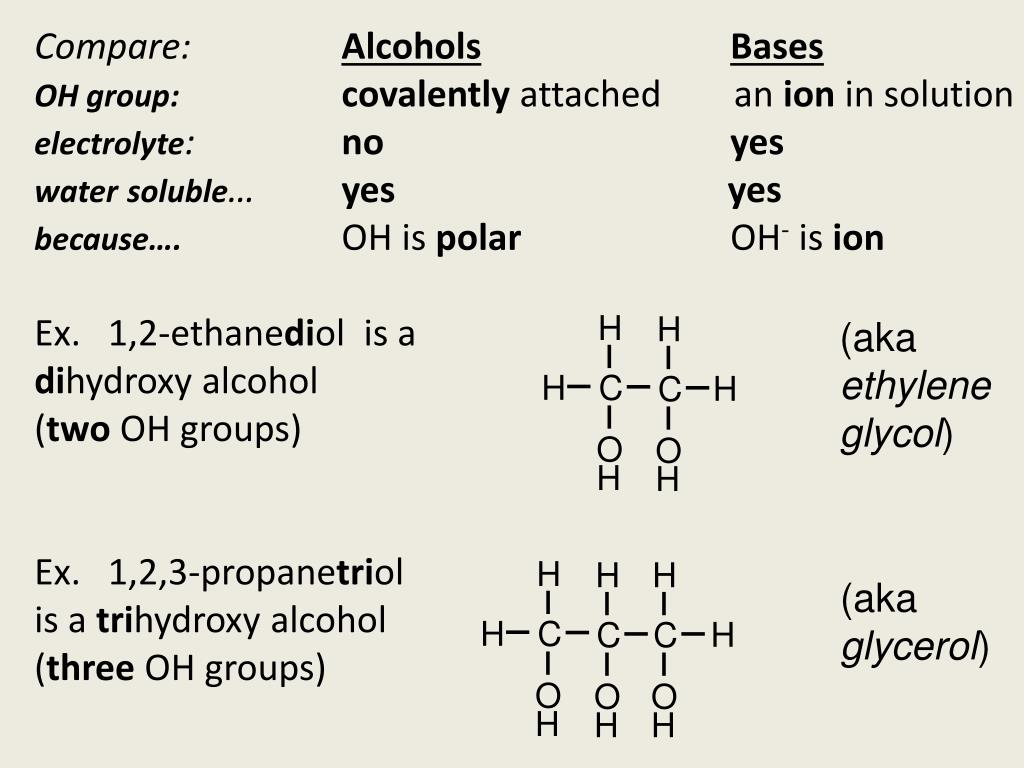
The homologous series of alcohols have the general formula C nH 2n+1OH.Īmong the most common organic compounds are alcohols. Alcohol is made by replacing a hydroxyl group with one hydrogen atom in an alkane. The ethyl group, for example, is the alkyl group in ethanol C 2H 5OH (or ethyl alcohol). Any class of organic compounds that include one or more hydroxyl (OH) groups linked to a carbon atom of the alkyl group is an alcoholic group.Īlcohols are organic water (H 2O) derivatives in which one of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an alkyl group, which is often represented by R in organic structures. Alcohols are organic compounds that include the alcohol group. The alcoholic or hydroxyl group is another name for the alcohol group. One oxygen and one hydrogen atom are joined together to form the alcohol group (-OH). Halogen atoms (Cl, Br, or I) serve as the heteroatom in haloalkanes. R-X is the formula for haloalkanes, where R is an alkyl group and X is the halogen atom. Haloalkanes have the general formula C nH 2n+1X, where X represents the halogens. Haloalkanes are formed when one hydrogen atom in an alkane is replaced with a halogen atom. The halo group is the abbreviation for the halogen group. The halogen group is another name for the halo group. Since chloromethane (CH 3-Cl) has the chloro group, bromomethane (CH 3-Br) contains the bromo group, and iodomethane (CH 3-I) contains the iodo group, the halo group can be found in chloromethane, bromomethane, and iodomethane. Since the elements chlorine, bromine, and iodine are collectively known as halogen, the Chloro, Bromo, and Iodo groups are referred to as halo groups and are denoted by the symbol -X. Halo groupĭepending on whether chlorine, bromine, or iodine atom is attached to a carbon atom of the organic compound, the halo group can be chloro (-Cl), bromo (-Br), or iodo (-I). The following parts go through each of these groups. The halo group, alcohol group, aldehyde group, ketone group, carboxylic acid group, alkene group, alkyne group are some of the most important functional groups in organic chemistry. A functional group is a group of atoms or bonds within a substance that is responsible for the substance’s distinctive chemical reactions. In organic chemistry, functional groups are the substituent atoms or groups of atoms that are connected to certain molecules. Arithmetic Progression - Common difference and Nth term | Class 10 MathsĪ functional group is an atom or a group of atoms that makes a carbon compound or an organic compound reactive and determines its properties.įunctional groups are atoms within molecules that have distinct properties regardless of the other atoms in the molecule.Area of a Triangle - Coordinate Geometry | Class 10 Maths.Chemical Indicators - Definition, Types, Examples.Class 10 RD Sharma Solutions- Chapter 2 Polynomials - Exercise 2.1 | Set 2.Euclid's Division Algorithm - Real Numbers | Class 10 Maths.Electric Potential and Potential Difference.Step deviation Method for Finding the Mean with Examples.Theorem - The tangent at any point of a circle is perpendicular to the radius through the point of contact - Circles | Class 10 Maths.


Section formula – Internal and External Division | Coordinate Geometry.ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
